Early detection is critical for effective diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer. It is important to recognize the warning signs of skin cancer and perform thorough medical evaluations of potentially harmful skin growths and abnormal lesions. Dr. Sabetta is well-trained in excision techniques that remove the growth in a way that maintains function without compromising aesthetics.
We offer a variety of surgical options for treating noncancerous, pre-cancerous, and cancerous moles and lesions. If you have additional questions or would like to speak with Dr. Sabetta, call 203-869-6111.
Understanding Your Treatment
Skin cancer screenings incorporate a thorough discussion of family history to determine your level of risk, as well as a precise skin examination to detect potentially harmful growths. For certain individuals, especially those who are considered “high-risk,” a full-body photography procedure (also known as “mole mapping”) may also be used to track changes in the skin that may indicate skin cancer. If a suspicious lesion is found, we will remove the abnormal growth(s) and examine the cells under a microscope. Once diagnosed, the method of treatment will depend on the type of cancer, the stage of growth, and the location on the body.
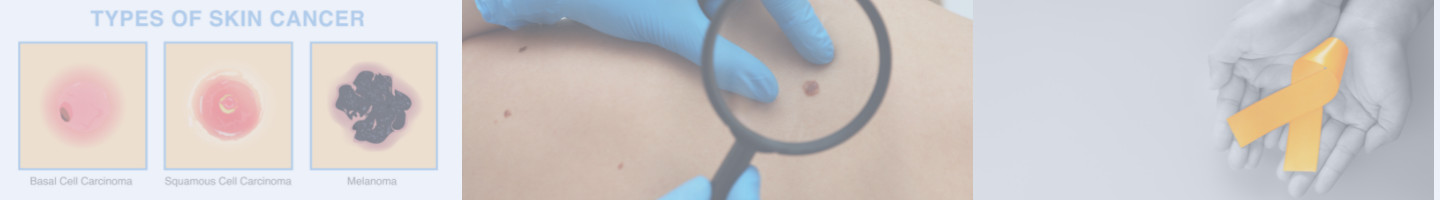
What are the different types of skin cancer?
The three most common forms of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Basal cell and squamous cell cancer are usually located on areas of the body that receive frequent sun exposure, such as the face, ears, or scalp. Basal cell cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin; squamous cell is usually confined to the skin but can metastasize, or spread through the body. Both of these forms can usually be easily treated with early detection.
Melanoma, on the other hand, is the most serious type of cancer due to its potential to metastasize. Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, even in areas that have little to no sun exposure, but often appears on the head or neck of men and the lower legs of women. A change in the appearance of moles or freckles is often a warning sign of melanoma, and patients are encouraged to see a doctor for suspicious skin tags. Surgery is usually needed to remove melanoma, and additional treatments may be necessary if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
To help prevent a recurrence of the cancer, a sufficient amount of tissue is removed to ensure that all the cancerous cells are excised. When appropriate, some patients are referred to an oncologist (cancer specialist) for additional treatment.
What are the risk factors?
Individuals with high levels of sun exposure and fair skin are at a greater risk for developing skin cancer. The risk of skin cancer is also greater for men than women, and older individuals are more at risk than younger individuals. Family history is another important contributing factor that our physicians take into account when performing skin cancer evaluations.
How can I protect myself?
Prevention is the best form of protection from skin cancer. Because sun exposure greatly increases your risk of developing skin cancer, proper sun care is essential. Follow these guidelines to reduce your chances of developing skin cancer:
- Limit your sun exposure during peak hours: 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Stay in the shade and plan outdoor activities for the morning or evening.
- Wear at least sunscreen, a wide-brimmed hat, or long sleeves every day – even cloudy days and during the winter.
- Protect your children. Most individuals receive 80% of their lifetime sun exposure before the age of 18.
Patients should perform regular skin self-exams at home, so that potentially cancerous changes can be addressed early. If you see anything suspicious, such as changes in a mole, schedule an appointment immediately .